How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to safety regulations. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, whether you’re a beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills.
Prepare for a comprehensive journey into the world of unmanned aerial vehicles.
We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, providing clear explanations and visual aids to help you understand their functions. From there, we’ll move through pre-flight procedures, safe takeoff and landing techniques, and the fundamentals of drone control. We will then progress to more advanced maneuvers and address crucial safety considerations and relevant regulations. Finally, we’ll discuss drone maintenance, photography/videography tips, and effective battery management.
This guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge and confidence needed for responsible and enjoyable drone operation.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section provides a detailed overview of key drone parts and a glossary of common terms. Furthermore, we will compare different types of drone batteries to help you make informed decisions.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone consists of several key components working in harmony. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and move in different directions. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this component receives data from various sensors and uses algorithms to control the motors and maintain stability. It is responsible for flight control, stabilization, and GPS navigation.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power to run the drone’s motors and other components. Battery life significantly impacts flight time.
- GPS Module: Allows the drone to determine its location and track its movements. Essential for features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and precise flight control.
- Camera (optional): Many drones include cameras for aerial photography and videography. Camera quality varies greatly depending on the drone model.
- Gimbal (optional): A stabilizing mount for the camera, ensuring smooth and steady footage even during flight maneuvers.
- Radio Transmitter/Controller: Used to pilot the drone and control its functions. It communicates wirelessly with the drone’s flight controller.
Glossary of Common Drone Terms
Familiarizing yourself with these common terms will enhance your understanding of drone operation and maintenance.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor individually.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement using accelerometers and gyroscopes.
- RTH (Return to Home): An automated function that returns the drone to its starting point.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a consistent altitude during flight.
- Failsafe: A safety mechanism that takes over control if communication with the controller is lost.
- Gimbal Lock: A situation where the gimbal’s freedom of movement is restricted.
- Firmware: The software that runs the drone’s hardware.
Comparison of Drone Battery Types

Different battery types offer various advantages and disadvantages.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques, I highly recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone . This will help you build a solid foundation in drone piloting, allowing you to confidently take to the skies and explore the possibilities of aerial photography and videography.
| Battery Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | High energy density, lightweight | Requires careful handling, can overheat, limited cycle life | 3.7V per cell |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | Higher voltage than LiPo, longer flight times | More expensive than LiPo, requires compatible charger | 4.2V per cell |
| LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | Safer than LiPo, longer cycle life | Lower energy density, heavier than LiPo | 3.2V per cell |
| Li-ion (Lithium-ion) | Relatively inexpensive, readily available | Lower energy density compared to LiPo and LiHV | 3.6V per cell |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is essential to ensure safe and reliable operation. This includes calibrating the drone’s compass and sensors and conducting a range test.
Pre-Flight Checklist

This checklist should be followed before every flight to mitigate potential risks.
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Verify the propeller blades are securely attached.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU.
- Perform a pre-flight range test.
- Check the GPS signal strength.
- Review local flight regulations and restrictions.
- Ensure you have a clear and safe flight area.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Calibration ensures accurate readings from the drone’s sensors, leading to stable and predictable flight. Improper calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior or crashes.
The specific steps for calibration vary depending on the drone model and its accompanying software. Generally, this involves following the instructions provided in the drone’s manual, often involving rotating the drone in a specific pattern to allow the sensors to self-calibrate.
Pre-Flight Range Test
This test determines the maximum distance between the drone and the controller before signal loss occurs. It’s crucial to understand this range to avoid losing control of the drone.
Start by slowly moving the drone away from the controller, monitoring the signal strength. Note the distance at which the signal weakens or is lost. This range should be well respected during all flights.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are paramount for preventing accidents. This section details the steps involved and discusses emergency procedures.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
- Ensure the drone is in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Slowly lift the drone vertically until it reaches a stable hover.
- Once stable, proceed with the desired flight maneuvers.
Safe Landing Procedure
- Begin descending slowly and steadily.
- Maintain a stable descent rate.
- As the drone approaches the ground, reduce the throttle gradually.
- Once the drone touches down, turn off the power.
Emergency Procedures
In case of unexpected issues, such as a loss of signal or malfunction, immediate action is critical. Familiarize yourself with your drone’s emergency procedures and practice them in a safe environment. Common emergency procedures include activating the Return-to-Home (RTH) function, if available, and attempting to regain control manually if possible. In some cases, battery failure may necessitate a controlled emergency landing.
Basic Flight Controls: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the functions of the control sticks and buttons on a typical drone controller is fundamental to safe and effective flight. This section provides a step-by-step guide for maneuvering the drone.
Control Stick and Button Functions
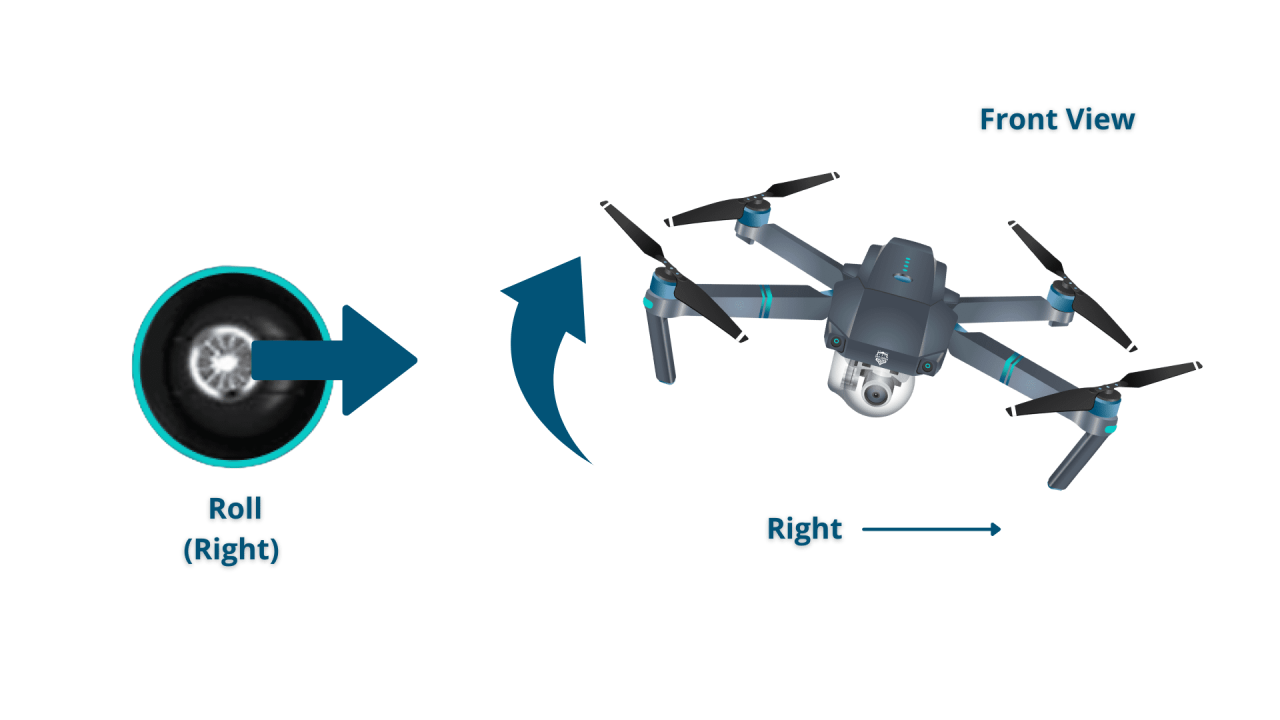
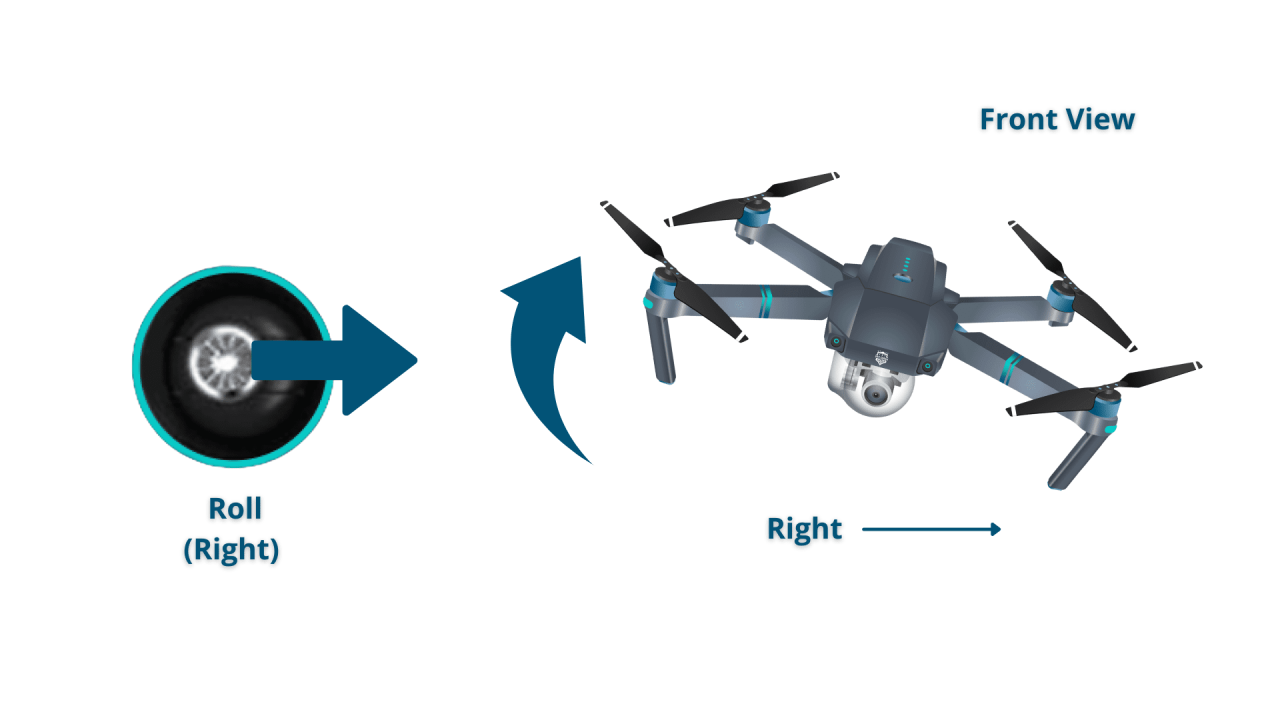
Most drone controllers use two joysticks. One typically controls the drone’s pitch and roll (forward/backward and left/right movement), while the other controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude).
Buttons on the controller typically control functions like takeoff, landing, Return-to-Home (RTH), and camera controls. The specific functions vary depending on the drone model and manufacturer.
Step-by-Step Maneuvering Guide
- Hovering: Maintain a steady position in the air by keeping the joysticks centered.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Gently push the left joystick forward to move forward and backward to move backward.
- Moving Left/Right: Gently push the left joystick left to move left and right to move right.
- Rotating: Use the right joystick to rotate the drone clockwise or counterclockwise.
- Ascending/Descending: Push the right joystick upwards to ascend and downwards to descend.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight situations.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Allows for faster speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and stability, helpful for long-range flights.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, even if the GPS signal is weak.
Advanced Flight Techniques
This section covers advanced maneuvers and considerations for complex aerial projects and challenging conditions.
Aerial Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers like flips, rolls, and spins require practice and skill. These are typically enabled through specific modes or button combinations on the controller, and should only be attempted in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people. Always prioritize safety.
Complex Aerial Photography/Videography Flight Plan
Planning a complex aerial project involves mapping out the flight path, considering lighting, composition, and potential obstacles. This usually involves pre-flight planning using drone-specific software, which allows for the creation of waypoints and automated flight paths.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Wind can significantly impact drone stability and control. Flying in windy conditions requires careful planning and skillful piloting. It’s recommended to avoid flying in strong winds. If flying in light to moderate winds is unavoidable, maintain a lower altitude, and be prepared to make quick adjustments to compensate for wind gusts. Always monitor wind speed and direction before and during flight.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Drone operation carries potential hazards and is subject to regulations. This section Artikels safety precautions and legal considerations.
Potential Hazards
- Collisions: Collisions with objects or people can result in damage or injury.
- Loss of Control: Loss of signal or malfunction can lead to uncontrolled flight.
- Battery Failure: Battery failure can cause the drone to fall unexpectedly.
- Privacy Concerns: Drones can be used to intrude on people’s privacy.
- Legal Issues: Operating a drone illegally can result in fines or legal penalties.
Local and National Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific laws and regulations in your area before operating a drone. These regulations often include restrictions on flight altitude, location, and proximity to airports or sensitive areas. Failing to comply with these regulations can lead to fines or other penalties.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation involves respecting privacy, adhering to regulations, and flying safely. This includes choosing appropriate flight locations, avoiding crowded areas, and always being aware of your surroundings.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are vital for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section provides a routine maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting steps.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule will help extend the life of your drone and prevent unexpected issues.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful planning and practice; learning the fundamentals is crucial before taking flight. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to enhance your knowledge and skills. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and consistent adherence to best practices.
- After each flight: Inspect for damage, clean the propellers and body, and check battery health.
- Monthly: Check all screws and connections, lubricate moving parts (if necessary), and update firmware.
- Annually: Conduct a more thorough inspection, including checking for wear and tear on internal components.
Cleaning and Inspection
Cleaning and inspecting your drone after each flight is crucial to remove dirt and debris. Use a soft cloth to clean the drone body and propellers. Inspect the propellers for any damage or cracks. Check all connections to ensure they are secure.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Some common malfunctions include motor issues, GPS problems, and battery problems. Consult your drone’s manual for troubleshooting guidance. If the problem persists, seek professional assistance.
Drone Photography and Videography
This section explains how to capture high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition, and lighting. Experiment with different settings to find what works best for your drone and the environment.
Camera Settings and Their Impact
Understanding the impact of settings like ISO, shutter speed, aperture, and white balance is key to achieving optimal image quality. Higher ISO values are better for low-light conditions but can increase noise. Shutter speed should be fast enough to freeze motion, but slow enough to allow sufficient light. Aperture controls depth of field.
Composing Effective Aerial Shots
Effective aerial shots require careful composition. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and using natural elements to create visually appealing images. Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
Battery Management and Charging
Proper battery care is crucial for maximizing battery life and ensuring safe operation. This section details charging procedures and tips for maximizing battery performance.
Importance of Proper Battery Care, How to operate a drone
Proper battery care extends battery life and prevents safety hazards. This includes storing batteries in a cool, dry place and avoiding overcharging or discharging.
Correct Charging Procedures
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging or using damaged chargers. Monitor the charging process to prevent overheating.
Maximizing Battery Life
Several practices can maximize battery life, including avoiding extreme temperatures, storing batteries at a moderate charge level, and not fully depleting the battery during each flight.
Drone Software and Apps
Drone software and apps enhance control and provide additional features. This section describes the functionalities of popular drone control apps and the use of simulation software.
Features and Functionalities of Drone Apps
Many apps provide features beyond basic flight control, such as intelligent flight modes, camera settings adjustments, and flight log analysis. Popular apps often offer features like waypoints, automated flight paths, and live video streaming.
Updating Firmware and Software
Regularly updating the drone’s firmware and software is important for improving performance, adding new features, and addressing potential bugs. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when updating.
Use of Drone Simulation Software
Drone simulation software allows pilots to practice flying in a safe and controlled environment. This can help improve skills and familiarize yourself with the drone’s controls before flying in real-world conditions.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the key aspects involved, from pre-flight preparation and basic flight controls to advanced techniques and safety protocols. By diligently following the steps Artikeld and prioritizing safe practices, you can confidently navigate the skies and unlock the full potential of your drone.
Remember that continued practice and a commitment to safety are crucial for becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
FAQ Insights
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a ready-to-fly (RTF) drone with GPS stabilization and beginner-friendly flight modes is recommended. These features help maintain stability and prevent crashes.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s advisable to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re flying in a new location or near magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
If your drone loses connection, most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that will automatically bring it back to its starting point. If this fails, visually locate the drone and attempt to regain control. If unsuccessful, contact relevant authorities if necessary.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Typical flight times range from 15-30 minutes, but this can be significantly shorter in windy conditions or with heavy camera use.